Challenge
At a restaurant, space allocated for seating is one of the most valuable assets to its profits. Recognizing that outdoor seating is wasted square footage during cold seasons, one client searched for a solution that would preserve yet improve the use of an existing outdoor dining area.
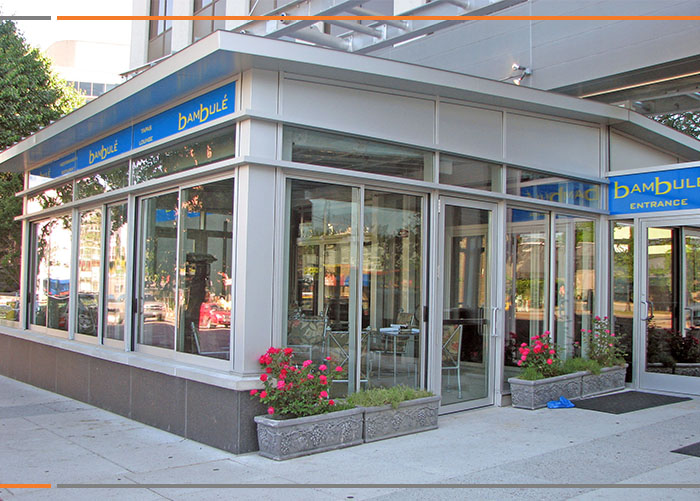
The restaurant sits along the first floor of a multi-level building in Washington, D.C. Outdoor seating fronting the building was bordered by a stone-capped concrete basewall. Initiating a dialogue with Solar Innovations® Architectural Glazing Systems, the client specified that the designed addition must insulate the occupants from cold weather, allow for ventilation in warm weather, and shelter diners from the elements.
Solution
Solar Innovations® collaborated with the client to create an ideal design that would resolve this challenge. The result was a straight eave lean-to unit with two gable ends and an overhanging standing-seam roof. The lean-to was to sit on the existing basewall and tie into a steel structure erected by the client. Two commercial out-swing doors were added to each gable end allowing patrons to access the space from the sidewalk. Sliding glass doors evenly divide the vertical faces of the lean-to structure. The sliding glass doors insulate the space in winter months and can open to create a free flow of air during summer months.
Many patrons are lured into the restaurant after seeing the inviting dining space created by the lean-to addition. This design unlocks valuable square footage for additional seating and gives the restaurant an edge over competitors who lack a flexible outdoor dining space. This case study exemplifies the benefits that can be gained in the commercial sector when utilizing the strategic designs offered by Solar Innovations®.
Project Details
Series: Straight Eave Lean-to Enclosure with 2 Gable Ends
Glazing: 1” Insulated Glazing